| a) Cutting |
| Shearing: Straight-line cutting using guillotine shears. |
| Laser Cutting: High-precision cutting with CNC-controlled lasers (CO₂ or fiber). |
| Plasma Cutting: For thick metals using ionized gas jets. |
| Waterjet Cutting: Uses high-pressure water (with abrasives for hard metals). |
| Punching/CNC Turret Punching: Creates holes or cutouts using dies. |
| b) Bending |
| Press Brake Bending: Uses a punch and die to form V-bends, U-bends, etc. |
| Roll Bending: For curved parts (e.g., cylinders). |
| Folding: Specialized machines create complex bends. |
| c) Forming |
| Stamping: High-volume production using dies (e.g., automotive panels). |
| Deep Drawing: Forms sheet metal into hollow shapes (e.g., cans, enclosures). |
| Hydroforming: Uses fluid pressure to shape metal. |
| Spinning: Rotates metal on a lathe to form axisymmetric parts. |
| d) Joining |
| Welding : MIG, TIG, spot welding for permanent joints. |
| Riveting : Mechanical fastening with rivets. |
| Adhesive Bonding : Uses industrial adhesives. |
| Clinching : Interlocking sheets without fasteners. |
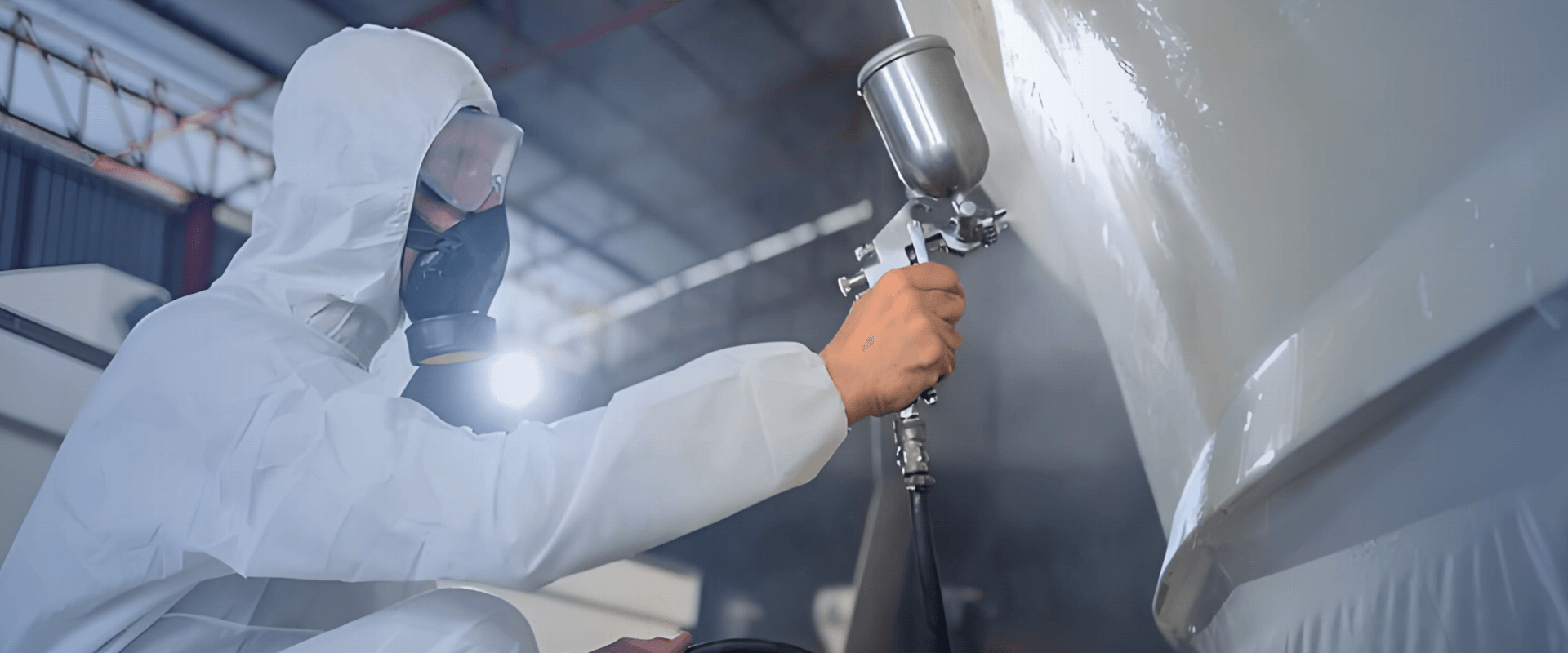
| e) Finishing |
| 2. Common Materials Used |
| Mild Steel (low-cost, weldable) |
| Stainless Steel (corrosion-resistant) |
| Aluminum (lightweight, good for bending) |
| Copper/Brass (electrical/decoration applications) |
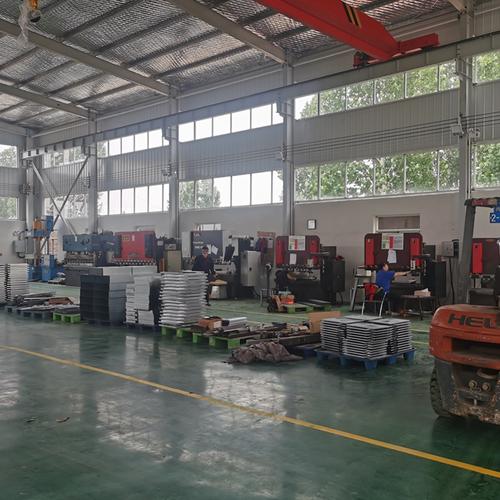
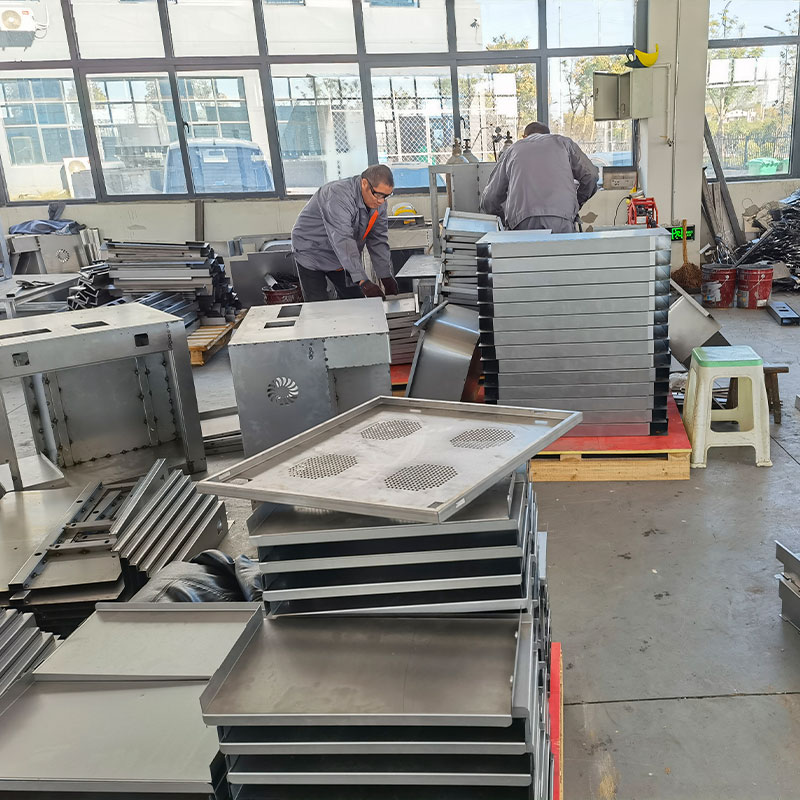
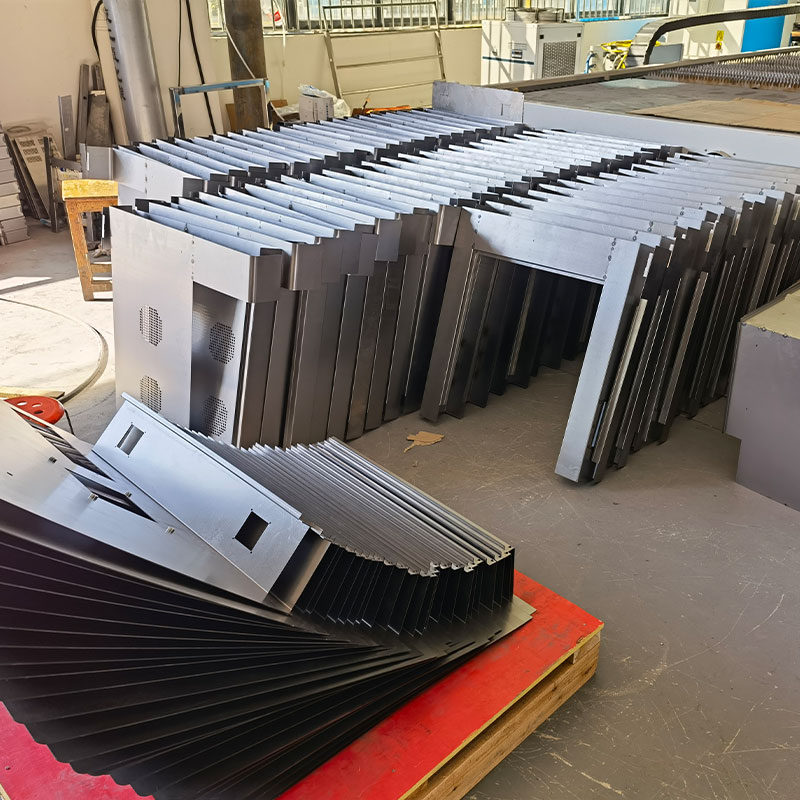
| 3,Metal Sheet shop and part of products display |